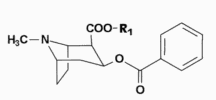
 Methylbenzoylecgonine, 2-Methoxycarbonyltropan-3-ylbenzoate
Methylbenzoylecgonine, 2-Methoxycarbonyltropan-3-ylbenzoate
C17H21NO4, M 303.4 g/mol
R1= -CH3: Cocaine, R1= -H: Benzoylecgonine
Szene terms: "coke" or "snow". Cocaine is a chemical excerpt from the sheets of the Coca bush (Erythroxylon coca), which grows particularly in South America and on the Indonesian islands. In the countries of origin the sheets of the Coca bush were chewed, in order to drive out hunger feelings and to produce euphorics. As illegal drug the crystalline Cocaine hydrochloride is usually sniffed, as the powder taken off as line (50 to 100 mg, price (2005) 50 to 80 €/g at 30-60% purity [EMCDDA]) with a pipe (straw or rolled up cash note) drawn into the nostrils. The cocaine consumption ranged, after cannabis, on the second place in Europe.
Cocaine is also injected intravenously. The mixture of Cocaine and heroin is called in the Scene as "Speed Balls".
Chemical active substance
Cocaine is the methyl ester of the benzoylated Ecgonine, which is related as Tropan alkaloid to atropine in nightshade plants. In the body hydrolysis of the methyl ester leads to Benzoylecgonine as main metabolite, as byproduct under co-operation of pseudo cholinesterase by splitting off the benzoyl group methylecgonine is formed. With preceding extended consumption of alcohol cocaethylene is formed.
Physiological effects
Cocaine affects particularly the nerves and narcosized the ganglia, making them insensitive to attractions. Therefore it was used in the medicine also for local anesthesia. Further physical effects are pupil dilation, step out of the eyeballs, pulse acceleration, intensified intestine. Weaker doses excite the central nervous system; it can come to typical Cocaine hallucinations such as skin itch, which seems caused by fleas, spiders or other small animals. With larger doses paralysis dominates, an anaesthizing effect, which extends also to the mucous membranes of the stomach. Thus hunger and thirst disappeared, it comes to loss of appetite and complete decrease in weight.
Psychological effects
Among other things deep fear conditions with illusions and hallucinations are predominantly unpleasant with the beginning of the consumption. Only after longer use, which leads also to a physical dependence, the intoxication is felt as benefit, e.g. increasing of the sexual desire feeling. Remarkably an increased movement urge and the inclination to incessant talking are connected with strongly lowered self-criticism. After fading away a "strong hang over" followed (frequently already after 1 hour) with removed, measure-courageous and sleepy feelings, similarly to a depression. An allergic reaction (anaphylactic shock) is discussed as relevant cause of Cocaine drug death.
Four stages of Cocaine dependence can be observed (H.W.Maier, 1926)
- acute Cocaine intoxication,
- chronic effects, frequently with continuing damages of the nervous system
- deliria with hallucinations, euphoria or pursuit ideas of the Cocaine,
- Insanity (intoxication psychosis): Consciousness is clouded, the environment is illusion distorted noticed, strong motor unrest could lead to assaults.
Metabolim / Detection
The detection of Cocaine in serum/plasma is limited for approx. 4-6 h (HT: 42-90 min.). In stored blood samples it decomposes without stabilizing addition of NaF and cooling within 2 days completely. As metabolites the hydrolysis products benzoylecgonine (HT: 5-7 h) and methylecgonine (HT: 4-5 h), which are both pharmacologically inactive, are detected. Hydrolysis is achieved by the enzyme butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) and two other liver carboxyxlesterases. In Urine the detection is possible by means of immunological quick tests (as Benzoylecgonine) for 3 to 5 days after the last consumption.
By means of hair analysis with GC/MS-detection, Cocaine and its metabolites are to be found as well as Coca ethylene up to 6 months.
Research
Until now, there is no way to treat a cocaine intoxication. As a new approach, an artificially produced butyrylcholinesterase is tested with an activity of around 2000fold higher than in the naturally occurring enzyme. This allows to reduce the HT of cocaine from 42-90 minutes at 1.3 to 2.7 seconds. Source: Zheng et. al, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 130 (36), 12148-12155, 2008.
History
Cocaine was first isolated in 1860 the german chemists Niemann. The psychiatrist Siegmund Freud examined his medical ability to use local anesthesia during surgery. The late Nobel laureate Richard Willstätter succeeded in 1902 in the synthetis of cocaine.
In 1886 Pemberton invented the famous Coca-Cola, which included an cocaine-extract until 1906. Afterwards it was replaced by caffeine.
End of the 19th century cocaine get a fashion drug in Europe because of its euphoric and motivational effects. Above all, artists and intellectuals sniefed cocaine, see arts and drugs.

